Trusted by:
What Are Digital Credentials and Why Do They Matter?
Digital credentials can provide organizations with a variety of benefits. What if you wanted to know them all at once? See this article!
AuthorSergey Butko
Updated: January 29, 2024
19 min read

Author
Sergey Butko
Updated: January 29, 2024
19 min read
Trusted by:
Diplomas and certificates from educational institutions and professional associations, ID cards and driving licenses, security clearances, and passports are all examples of paper credentials.
The problem with these physical credentials is that they can be lost or stolen, causing a wide range of inconveniences.
In this article, we will explain the types of digital credentials and how organizations and professionals can benefit from comprehensive learner records and digital credentialing.
What are Digital Credentials?
Digital credentials are digital certificates issued by education institutions as proof of authenticity, achievements, and learning.
In function, these are no different from paper credentials. As you would present your passport or a driving license, you need to prove the necessary qualification when you apply for a new job.
In today's world dominated by online apps, web pages, and social media, you need to present proof instantly.
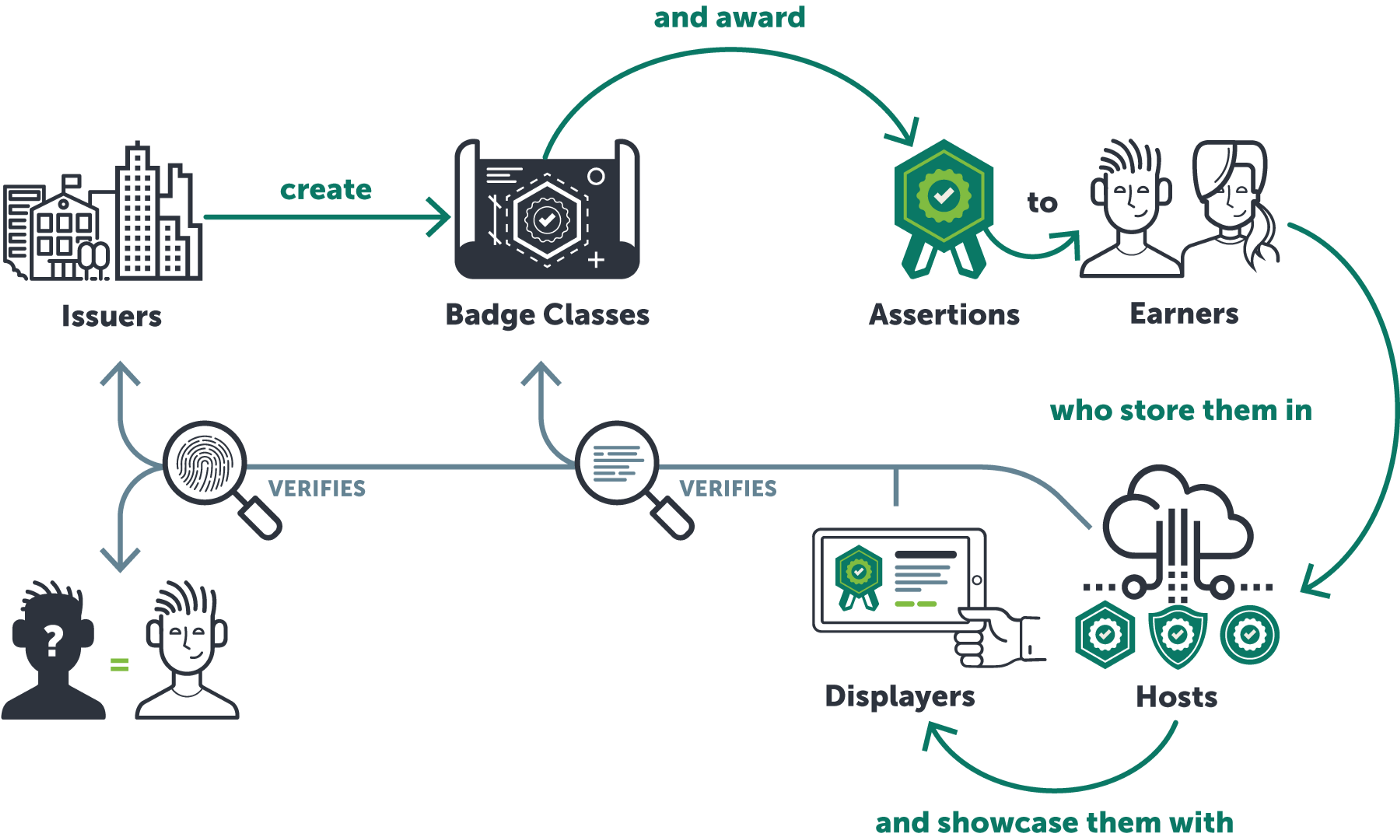
Instead of asking your academic institution for paper copies of academic credentials that you need to pay for, or PDF copies that are easily forged by other candidates, you can resort to digital technologies.
The most common examples include:
College degree certificates issued by educational providers
Acknowledgments for understanding a complex topic
Academic credit for applicable work experience
Awards for mastering a personal or professional skill
Corporate education
However, online credentials are also used for:
Proof of membership
Awards for achievement, behavior, and effort.
While it may seem like creating a digital credential is a hassle, it can actually be pretty simple and straightforward with a tool like Certifier.
Still not sure? We'll explain it further in this article ➡️ What's the Difference Between a Certificate, Credential, and a Degree?
Types of Digital Credentials
There are three types of online credentials: digital badges, micro-credentials, and digital certificates. All three types revolve around the same concept that digital credentials provide a better link to opportunities than even secure transcriptions on paper currently.
Digital Badges
Digital badges were pioneered by the Mozilla and MacArthur foundations as a way of recognizing skills acquired outside the formal educational system.
They are usually awarded by academic institutions, like community colleges, online course providers, or by organizers of events and conferences.
Digital badges are digital verifiable credentials that contain:
The issuer identity
The name of the recipient
Award criteria
Issue Date
Evidence of learning
By accessing the information contained in the digital badge via a QR code or URL link, an interested party can verify and certify the acquired skills and identity of the holder.
Digital badges are typically used for credentials that take a short time to learn, such as qualification modules,
They can use shapes, colors, and symbols to identify levels of achievement.
These credentials are designed so they can be easily embedded across a variety of platforms. Learners can share their digital badges on social media, email signature, online portfolio, resume, etc.
Companies can choose to use only digital badges, digital certificates, or both.
A digital badge can be awarded for:
Completing a project
Verifying specific commitments such as a blood drive badge
Valuing skills, such as mastery of the Javascript
Certifying the completion of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)
Micro-credentials
Micro-credentials are certifications that attest to the learning outcomes of a short course or module, which is assessed in a transparent matter.
These micro-certificates allow for flexible, modular learning and can be used throughout the learner's professional career. Sometimes they take the form of badges.
Training organizations can use digital micro-certificates to verify the mastery of different blocks of competence that make up a training course or a webinar.
Micro-credentials allow learners to claim their professional skills throughout their careers. They can present micro-certification during job interviews or use them for professional development within the company.
Micro-credentials are designed to promote mobility and flexibility in the authentication of learning.
Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are non-material, and unlike paper certificates, they are easy to share and hard to misplace.
What is more, digital certificates have many benefits for training organizations, as they allow them to:
Streamline administrative processes
Store documents and related data
Quickly access information at requests
Showcase an institution's innovative approach
Build stronger bonds between alumni and the university
Prevent diploma falsification and thus protect the organization's reputation
Let's take a look at one example:
Emlyon Business School, based in Lyon, France is the first business school that begins awarding digital certificates to its students and alumni. Since 2019, this school's diplomas and certifications have been automatically delivered and micro-certified on the blockchain framework.
To access their digital certificate, students use a unique URL link that contains all the necessary information that demonstrates their training credentials. This allows holders to share these academic credentials with recruiters, companies, and audiences on social media.
Basing digital credential services on blockchain technologies comes with unique advantages. Blockchain-certified academic credentials are 100% secure, tamper-proof, verifiable, and permanent. The public certificate blockchain is a decentralized database that is, by its nature, forgery-proof. Digital credentials and academic transcripts are stored securely because blockchain information is impossible to falsify.
Role of Anonymous Digital Credentials
The idea behind anonymous credential systems is that users receive cryptographic tokens that allow them to prove qualifications and relationships with organizations anonymously. This is a much more private alternative to maintaining lase centralized user records.
Paper world analogs of non-anonymous credentials like passports, driving licenses, and credit cards contain the name of the owner and have some type of authenticating information like a signature, PIN, or photo.
Paper world analogs of anonymous credentials are money, bus tickets, and game tokens.
Since these credentials don't have any personally identifying information, they can be exchanged between users without the issuers or relying parties being aware of that.
Let's explore the properties of both types of credentials using the example of money vs. a credit card.

Money is protected from forgery by its physical attributes. But beyond that, very little information is available. Coins have the year of minting, and banknotes have serial numbers as required by law enforcement.
Credit card use, on the other hand, is conditioned by the creation of highly detailed digital records about the card owner. This means that user communities don't have the kind of privacy they have with money.
The introduction of pseudonyms is an extension of anonymity. Pseudonyms allow organizations to associate users with accounts without the ability to determine their real identities.
Apart from pseudonyms, anonymous credential systems use another cryptographic protocol – blind signatures. In these schemes, the signer never learns the message they sign nor the signature the recipient obtains.
Blind signatures are an important part of many privacy-sensitive applications such as anonymous payments, voting, and credentials for institutions.
Another credential form that brings new features to anonymous credentials is multi-show unlinkability.
Using a group signature scheme, group members can sign a message with their respective secret keys.
This signature can be verified by someone who knows the common public key, but it doesn't reveal any information about the signers, save the group membership.
What Are the Benefits of Digital Credentials?
Saving Resources
By shifting to digital credentials, businesses can save time and money. while freeing up resources for teams to develop skills that:
Support workforce development
Help grow the company
Improve customer experience.
For example, the Digital Marketing Institute managed to cut the time spent issuing credentials by 93.75%. After the digital transformation, the monthly workload of at least 8 hours dropped to half-hour of work while boosting team productivity.
✅ Verifiable
Verifying qualifications is a complex and time-consuming process. Paper certificates are easy to misplace or get damaged, and more often than not, employees rely on candidates to provide proof of qualification for critical skills.
Digital credentialing simplifies the process by:
Providing one-click verification
Saving time for the HR team
Being very hard to fake
In one study, 1,000 US professionals were surveyed about the accuracy of their resumes. About 30% of participants said that they "bent the truth" about their skills and experience.
✅ Automated
Issuing digital certificates and badges is simple and efficient because the administrative process is pretty much automated. Incorporating digital credentialing software into existing workflows can save hours of admin time each day. Made possible by a capable API and Zapier, custom integrations can take place across many of the leading Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Design and spelling mistakes always create extra costs when issuing physical academic degree credentials.
Fixing one certificate is not a big deal, but repairing hundreds or thousands doesn't come cheap. By automating the credential form, organizations can:
Automate typo correction. Let's say that recipients notice a spelling mistake in their name and submit a correction request. Instead of having a team member manually review requests, such small typos are automatically corrected by the credential platform.
Retroactively amend the design. Digital technology allows you to amend an existing certificate design and update all digital certificates with just one click.
For example, McGraw-Hill created a set of digital badges taking inspiration from the belts used in karate. After the first batch was published, they added L1, L2, L3, and L4 to represent different badge levels and circled the relevant value on each badge.
Using a digital credentialing platform, they managed to make the change and update all their previous badges with ease.
✅ Portable
Digital badges that are compliant with the OpenBadge digital identity standards can be added to existing badge backpacks.
Backpacks are the central place to manage, display, and organize digital badges. If they need convention verification in the field, recipients can upload their digital badges to digital wallets, like Apple Wallet and Google Pay. This way, individuals can easily provide credentials on-demand or prove an association membership.
Imagine you're attending an interview for a new job. The interviewer reviews your resume and asks for details about modules for a listed qualification.
You refer to your digital wallet that holds your digital badge. You take advantage of this simple situation to:
Provide proof of qualification
Inform the interviewer about your knowledge
Opened up a conversation topic about other digital badges you hold
✅ Shareable
Students work hard to achieve their qualifications through the learning experience. When they reach their goal, they rush to share the good news with friends and family. Digital certificates are easy to share on social media, through email signage, or on a webpage.
This gives several advantages over paper world analogs:
Trackable real-time engagement and views of digital badges and certificates
Increasing awareness for programs and courses, as well as the businesses with digital certificates
Improving holder employability by sharing electronic credentials to LinkedIn profiles.
How to Protect Digital Credentials from Being Forged
One of the major challenges of the digital world is that digital formats are easy to copy. Another candidate can take a peek at your digital certificate online, take a screenshot, change the name in an editing tool, and present it in the job race just as you.
That was the case with the old digital technology that relied on sharing image or document files in formats like JPG, DOC, or PDF.
These formats are not secure enough, and still sharing a visual image remains the fastest means of communication.
So how can you share visual files without them being forged? By using the latest conception of the internet, called Web 3.
The first conception was Web 1.0, or read-only web. Web 2.0 was known as the interactive, collaborative, or sharing web. This is what most of us recognize today. Social media platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter are based on it.
Now we are witnessing the emergence of Web 3.0 or the "semantic web" that brings together artificial intelligence chatbots and virtual assistants, the 3D digital iteration of the physical world known as metaverse, secure encryption of digital items, public key infrastructures, and data using blockchain technology.
This version of the web allows data to be not only accessed (Web 1.0) and shared (Web 2.0) but also verified by humans and machines.
Now we can embed an image or badge of a college degree certificate on a website or a social media page and have instant means for external verification.
Use cases of Digital Credentials
Over time, digital credentials have evolved from a whiteboard concept to a game-changer standard that supports many important education trends.
Improved Badges
When the open badge initiative was launched a decade ago, anyone could award a badge for anything. This situation exploded digital credentialing and improved signaling for learners but came at the expense of quality.
K-12 education has been a champion of badges, typically called micro-credentials, in professional learning.
For example, Digital Promise is issuing more than 450 micro-credentials that develop and verify different educator skills.
Bloomboard uses micro-credentials to support the professional learning system at Harmony Public Schools, which is a good example of a comprehensive talent development system.
For example, IBM has been issuing digital credentials that support important skills with trusted assessments.
Improved Degrees
A shift to skills-based hiring and tangible value for college degrees has prompted many institutions to make current degree programs better and present valuable skills.
Online higher education leaders like SNHU and WGU are already back mapping courses and degrees from job critical skills. Their courses are consistent with content and incorporate assessments that validate skills.
Improved Transcripts
Mastery Transcript Consortium is a network of more than 330 innovative schools in the US that have agreed to issue more meaningful transcripts that include demonstrations of mastery rather than just listing classes and grades.
Another organization, Greenlight Credentials, helps north Texas high schools build and permit a digital profile to employers and postsecondary institutions. The extended transcript incorporates traditional and new forms of evidence of learning, with add-ons that help learners tell their stories.
Improved Records
Learners are accessing multiple providers inside and outside degree programs. They are learning for life across a range of employment experiences, so they need portable interoperable records.
For example, Walmart and Salesforce developed pilot solutions that would help over two million workers capture and communicate what they are learning.
The system they came up with maintains a record of the skills required to earn each badge, and since the data is machine-readable and interoperable, it gives learners portability across institutions and employers.
Improved Incentives
A blockchain record like Greenlight Credentials can automatically execute contracts that make attainment incentives available to learners. Learners can automatically have digital curriculum standards shared on a LinkedIn profile where they are discoverable and machine-readable.
This way, if a learner gave a group of employees access to their Greenlight Credentials profile, they could automatically receive work-based learning and employment offers.
Wrapping up
Digital credentials bring consistency, data, and security to skill capture and presentation. They give learners the ability to manage their skill certificates and academic record in a portable and verified way.
On the other hand, employees who have access to digital credentials are well-positioned to make more efficient hiring practices.
Finally, organizations that issue digital credentials for learning are in a position to not only expand their programs but also contribute to the future of business.
Are you looking for a way to create credentials for your business, course, training, or something else? We have just what you need!
Sign up for Certifier for free and create your first credential in as little as 15 minutes, and wow your participants while giving them a credential they can show off!

Sergey Butko
Tech entrepreneur. Forbes 30 Under 30 Europe. At Certifier, Sergey’s work focused on revolutionizing the way credentials, certificates, and badges are issued and managed through cutting-edge APIs and software infrastructure.
Sergey Butko
Tech entrepreneur. Forbes 30 Under 30 Europe. At Certifier, Sergey’s work focused on revolutionizing the way credentials, certificates, and badges are issued and managed through cutting-edge APIs and software infrastructure.
Share this article